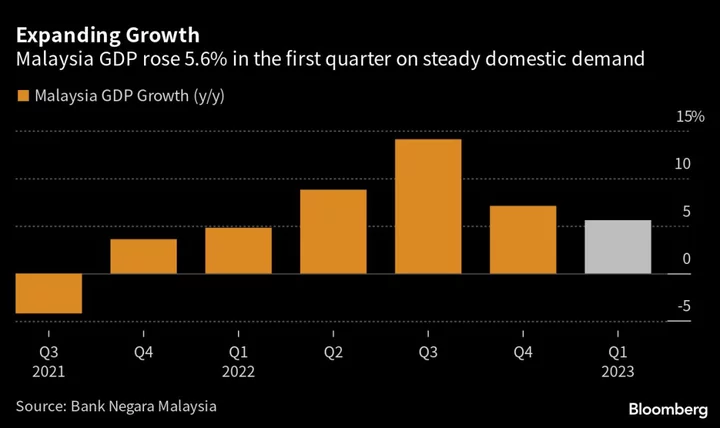
Malaysia’s economic growth beat expectations in the first quarter of the year, with robust domestic demand justifying the central bank’s recent move to return borrowing costs to pre-pandemic levels.
Gross domestic product for the January-March period expanded 5.6% from a year ago, data from Bank Negara Malaysia and the Department of Statistics showed on Friday. That’s faster than the median estimate of 5.1% growth in a Bloomberg survey. On a sequential basis, GDP returned to positive territory at 0.9%.
The economy’s resilience in the face of a global slowdown vindicates the central bank’s surprise resumption of policy tightening last week to manage inflationary pressures. It is also in line with the official forecast for growth to come in between 4% to 5% this year amid a challenging world outlook.
The increase in benchmark interest rate was meant to keep inflation in check while the economy grows, according to a statement from BNM. The central bank maintained that its rate moves have been gradual and measured, while signaling future actions will depend on growth and inflation data.
“The economy is no longer in crisis and has in fact continued to gain strength,” BNM Governor Nor Shamsiah Yunus told reporters in Kuala Lumpur. “It is necessary and warranted that the policy is recalibrated to make sure that we continue to be on a sustainable growth path.”
Underlying private consumption, along with on-going large infrastructure projects, are poised to continue to be Malaysia’s key growth drivers, offsetting the impact from moderating exports. Business activity in Malaysia has continued to grow, with the jobless rate remaining at a three-year-low for a second straight month in March.
Risks to growth going forward remain predominantly external, such as weaker-than-expected global growth and more volatile global financial market conditions. March’s outbound shipments contracted for the first time in 31 months amid softening external demand.
The central bank reaffirmed the 2023 inflation forecast, with price gains seen averaging between 2.8% to 3.8%.
The inflation forecast includes further subsidy rationalization, including fuel and electricity. The authorities cited higher global commodity prices due to geopolitical tensions and adverse weather events as top risks to the price outlook, while weaker global growth and fading pent-up demand are the downside risks.
--With assistance from Ravil Shirodkar, Cecilia Yap, Tomoko Sato and Kevin Varley.